Web Hosting is a fundamental part of a live website. In simple words, it’s your site’s place on the Internet. The term “hosting” refers to the service provided by companies whose server (or cluster of servers) is hosting your website files (HTML, CSS, images, videos, etc.) for users to access on the web.
Web Hosting isn’t tricky until you realize that numerous companies offer various hosting solutions. And when you’re not sure what hosting solutions you need, that can throw a beginner off course. So, what kind of hosting is right for your website? How do you make the best choice for your business needs? This guide to web hosting will cover the basics and introduce you to the different hosting solutions available on the market.
3 Things You Need to Take Your Website Live
a. Your actual website content (files that make up your site)
b. Web Hosting services from a reliable web host (company hosting your site)
c. Domain name registered with a Domain Registrar (organization providing your website a unique name)

You can use two different providers for the two separate services (hosting and domain registration), but there are many hosting companies offering them together as a package.
First, the fundamentals!
Website and Web Server
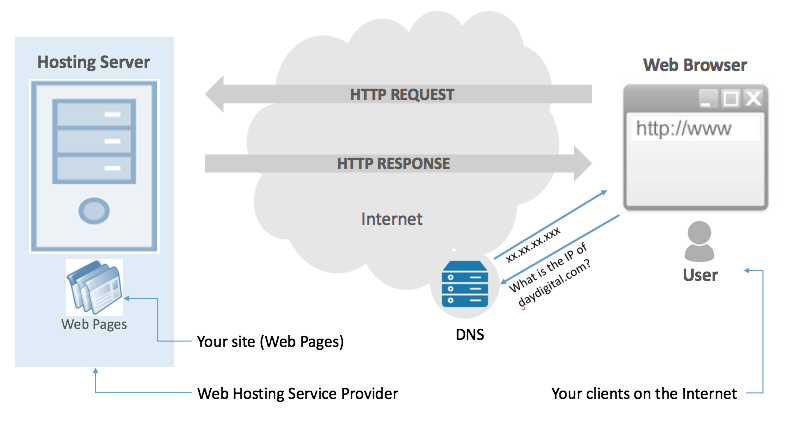
A website is a collection of web pages accessible through the Internet. If you wish to have a website, you should have it published on at least one web server. A web server completes the function of storing, processing and delivering your web pages to your users on the Internet.
When your clients type your web address in their browsers, their computer will connect to the web server. The web server will process the request and deliver the web pages.
What is Web Hosting and Who is a Web Host?
Most individuals and organizations do not have web servers of their own. They rent out space in servers maintained by a third-party company specializing in the business of providing the technologies and services required to host websites.
Web Hosting is the service that will empower you to have your web pages “hosted” and “served” to your users on the Internet, without having to worry about running or maintaining web servers.
A web hosting service provider (web host) is the name given to third-party companies offering Web Hosting services.
What is Web Hosting?
Web Hosting and Data Center: Are They The Same?
Technically, they are different. Web Hosting is the term used for the services offered to store and serve your site on the Internet. Data Center refers to the infrastructure utilized by the hosting company to facilitate the hosting service. It includes a large group of networked servers, telecommunications systems, backup power supplies, security devices and other equipment required to provide the hosting service.
Domain Name and DNS
A “domain name” is a unique name identifying your site on the Internet. It is the name people will use to reach your site from the web browser. For example, daydigital.com is our domain name. A DNS (Domain Name Server) translates this human-readable name into a numeric IP (Internet Protocol) address that computers, routers, and other networking components understand.
Domain Registration and Registrar
Domain Registration means securing your domain name on the Internet so that nobody else can use it. A Domain Registrar offers these registration services along with DNS. There are several major factors to consider before you choose a Registrar. Some of them are:
- ICANN Accreditation
- Security
- Domain Transfer
- Control Panel
You can buy your domain name from a stand-alone Registrar or from companies that provide domain registry services along with web hosting.
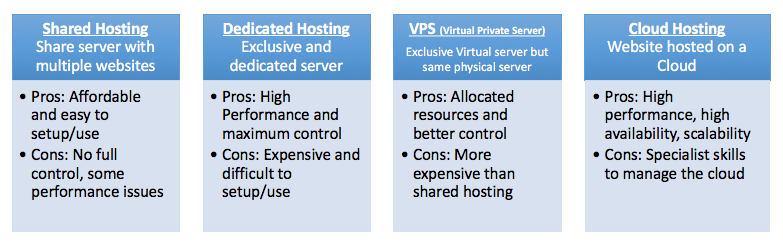
What Are the Different Types of Web Hosting?
There are four main types of Web Hosting, and each option comes with its pros and cons.
- Shared Hosting
- Dedicated Hosting
- VPS (Virtual Private Server)
- Cloud Hosting
Shared Hosting
As the name implies, you share the hosting server with many other sites. Usually, there is a collective pool of resources (RAM, CPU, Disk space) that all sites hosted on the server share and use.
Pros
Shared Hosting is recommended for websites with moderate traffic (which most websites are) because the cost is low, it is easy to get started with and does not require any technical knowledge.
Cons
Because you are sharing the resources with more websites, performance may be affected when there are spikes. There is no root access (ability to fully control your server).
Shared Hosting is the most popular hosting plan and usually the most affordable too.
Dedicated Hosting
You rent an entire server exclusively for your usage from the hosting provider. You get your dedicated server, and you don’t have to share any server resources (CPU, RAM or Disk space) with any other sites.
Pros
You get better and assured performance along with maximum control of the server.
Cons
Obviously, the costs are high, and you will have to take more responsibility for managing the server. With great freedom comes great responsibility; and in this case, higher costs too!
VPS (Virtual Private Server)
As the name implies, you rent a “virtual” server as your private server. In reality, you are sharing the physical server with other websites. By using a computing technique called virtualization, the server resources are abstracted and partitioned to emulate multiple virtual servers that may be individually controlled by each VPS user. A virtual server is logically private (each running its own operating system) but physically not.
Pros
Although you are still sharing the physical server (resources) with other websites, you have a fixed quota allocated exclusively to you. You may also have root access and more power over controlling your virtual server.
Cons
It is more expensive than shared hosting. Your site performance may still be affected if there is very high traffic.
If you cannot afford dedicated server hosting, but would still like to get some level of control and an assured allowance of server resources for better performance, you should consider VPS.
Cloud Hosting
The latest trend to hit the hosting market and probably the most advanced option is Cloud Hosting. Using “Cloud Computing,” a group of servers (referred to as a cloud) works together to act as one large server.
Pros
You only pay for what you use on the Cloud. So you could have traffic spikes (say during a particular season) and you wouldn’t have to worry about not having a dedicated server. Cloud Hosting is the most scalable hosting solution while also being very cost effective.
Cons
You need cloud experts with technical knowledge to manage your cloud hosting solution.
If your business demands high performance and high availability along with scalability, cloud hosting is an option for you.
So if you are about to take your new website live and feeling overwhelmed by all the hosting options, this guide to web hosting should help you make an informed decision. The growing number of packages offered by web hosting companies can make anyone feel lost!
It’s up to you to decide the right web hosting solution for your business. But remember, there isn’t anything like one perfect hosting plan for all sites! You just have to pick the right hosting type for your needs.